
Table of Contents
What is the latest trend in industrial cooling?
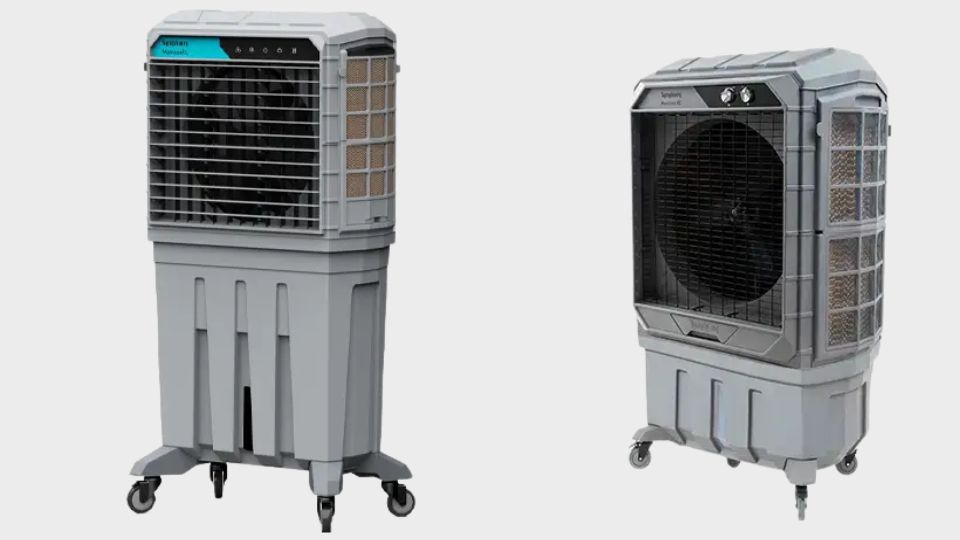
For decades, the Indian industrial landscape was dominated by fabricated metal coolers – heavy, boxy, and prone to rust. However, recent years mark a definitive shift in commercial air cooling. The market is rapidly moving toward Big Size Plastic Coolers (Rotomolded variants) as the new standard for efficiency and durability.
Facility managers are no longer looking for just “cooling”; they are looking for “climate control assets.” This evolution is driven by material science. The big size coolers for industries and commercial applications in the modern market are no longer welded from steel sheets; they are scientifically engineered from high-density polymers. This transition isn’t just aesthetic – it is a fundamental upgrade in how industries manage heat, hygiene, and energy costs.
Why are Food and Pharma Warehouses Banning Metal Coolers?
In hygiene-critical sectors, air quality is as important as air temperature. This raises a critical question for compliance officers: Is your cooling equipment contaminating your product?
Traditional metal coolers eventually corrode. As the galvanized layer wears off, fine rust particles can become airborne, circulating through the facility. For pharmaceutical plants and food processing units, this is a nightmare scenario that violates strict hygiene protocols.
This is why FDA and HACCP-compliant facilities are switching to the modern plastic air cooler. High-grade engineering plastic is chemically inert, non-porous, and rust-proof. It can be washed down with strong disinfectants without corroding, ensuring that the air delivery remains pure. When searching for the best air cooler for factories or clean rooms, a washable plastic body is now the non-negotiable standard.
How Do Molded Curves Improve Airflow Efficiency?
One of the most overlooked technical advantages of a big size plastic cooler is its aerodynamics.
- The Metal Problem: Metal coolers are typically “fabricated.” This means sheets are cut and welded at 90-degree angles. These sharp corners create internal air turbulence and drag, forcing the fan to work harder to push air out.
- The Plastic Solution: Plastic coolers are “molded.” This allows for smooth, scientifically designed internal curves that mimic a wind tunnel.
This seamless design reduces air resistance, allowing the fan to deliver higher CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) with less electrical drag. The result is energy-efficient large space cooling that throws air further and faster than a boxy metal competitor, simply because the air has a smoother path to travel.
Read Our Article: Portable Cooling System: Everything You Need to Know
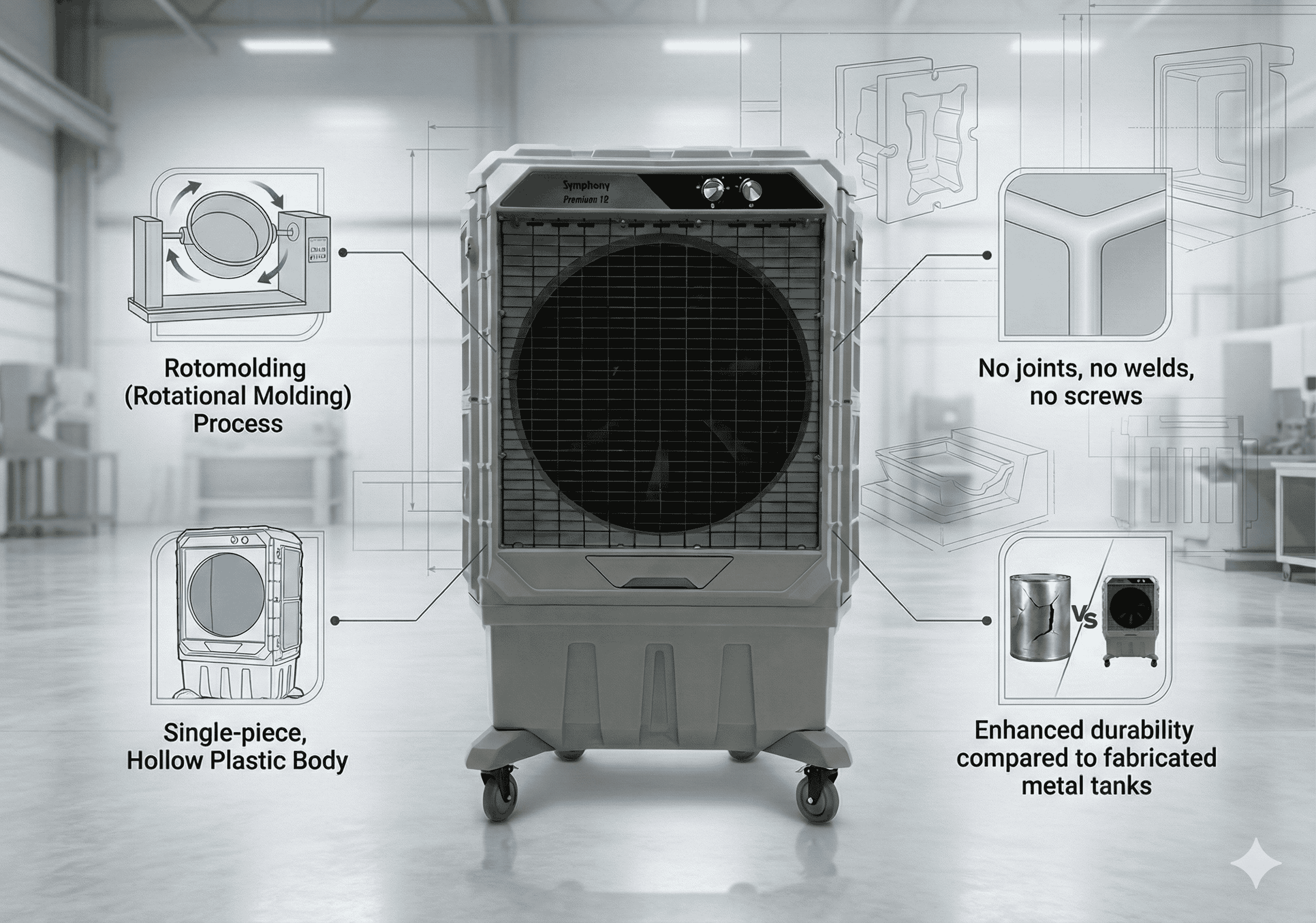
What is the Advantage of Rotomolded Coolers over Fabricated Metal?
When evaluating plastic vs metal industrial coolers, the manufacturing process tells the real story of durability.
Most big size cooler models made of plastic utilize a process called Rotomolding (Rotational Molding). This process creates a single, hollow piece of plastic with no joints, welds, or screws holding the main tank together.
Why does this matter?
- Leak-Proof: No welded joints means there are zero weak points for water to leak through after years of vibration.
- Vibration-Free: Metal panels often rattle and loosen over time due to fan vibration. A solid rotomolded body absorbs vibration, leading to significantly quieter operation.
- Impact Resistance: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is tough. It can take heavy impacts on a rough shop floor without denting or cracking, unlike sheet metal.
Why Are Plastic Coolers Better for Coastal and Chemical Industries?
Geography dictates the lifespan of your machinery. In coastal industrial hubs like Surat, Mumbai, and Chennai, salty sea air is a silent killer of infrastructure. A standard Galvanized Iron (GI) cooler body can begin to rot within 24 months in these saline environments.
A big size cooler made of UV-stabilized polymer is immune to this issue. Plastic does not react with salt or humidity. Furthermore, in chemical industries where acidic fumes are present, plastic bodies offer superior resistance compared to metal, which would oxidize rapidly. For a factory owner in a coastal zone, choosing a polymer body is the only way to ensure the machine lasts 10+ years.
Are Plastic Coolers a Better Investment than Metal Coolers?
When CFOs ask about the ROI of an industrial air cooler, the answer lies in “Agility” and “Resale Value.”
- Weight vs. Workflow (Agility) Modern manufacturing is agile; production lines shift and layouts change. A massive metal cooler is effectively a permanent fixture – once installed, it is too heavy to move easily. In contrast, a big size plastic cooler is significantly lighter relative to its size. Mounted on heavy-duty castors, these units become mobile assets that can be wheeled exactly where your workers are operating that day.
- The Hidden Resale Value Analyze the 5-year outlook. A metal cooler, after five years of exposure to water and heat, is often rusted and deemed “scrap metal.” It has near-zero resale value. A high-quality plastic cooler, however, retains its shape and aesthetics. A simple wipe-down restores it to a “like-new” look, commanding a much higher resale value on the secondary market.
What is the Future of Commercial Cooling Technology?
The era of the “rusty box” is over. The industrial and commercial coolers dominating the market in coming years and beyond are smart, sleek, and scientifically built polymers.
We are already seeing the rise of “Smart Plastics” – coolers integrating IoT sensors for humidity control and digital displays, features that were impossible to seamlessly integrate into crude metal fabrications.
Conclusion
For business owners and purchase managers, the choice is clear. To ensure the wellness of your workforce and the efficiency of your plant, stop buying fabrication. Start investing in engineering. Switch to Big Size Plastic Coolers – the future-proof solution for modern industry.
The Role of Symphony Venti-Cool
While unorganized manufacturers still weld massive metal boxes, brands like Symphony have standardized the “Large Space Venti-Cooling” (LSV) concept with Venti-Cool series. This range serves as the prime example of why engineering plastic is superior for industrial applications.
The “Modular” Role: Unlike traditional centralized metal plants that require massive rooftop construction, Venti-Cool units (like the VC 20U or VC 25U) act as modular blocks.
- If a factory expands, they don’t need to rebuild their cooling plant. They simply add another Venti-Cool module. This “scalability” is a key management advantage over static metal fabrications.
The “Hygiene” Role: For the Food & Pharma sectors mentioned in this article, Venti-Cool is the often-cited solution.
- Its UV-Stabilized Engineering Plastic body prevents the rust contamination issues common with Galvanized Iron (GI) coolers. It provides the “clean air” compliance required by HACCP/FDA standards.
The “Energy” Role:
- With models delivering up to 25,000 CMH (Cubic Meters per Hour) of airflow on just 1.1kW to 1.5kW motors, it demonstrates the aerodynamic efficiency of molded plastic over boxy metal.
Read Our Article: Outdoor Cooling System for Urban and Industrial Climate Control
FAQs on Big Size Plastic Coolers
Why are Industries Switching to Big Size Plastic Coolers? The Future of Industrial Cooling
Does the body material actually affect the cooling performance?
Yes, significantly. Research into material thermodynamics shows a massive difference in thermal conductivity.
- Galvanized Steel: Has a high thermal conductivity (~50 W/mK), meaning it easily transfers outside solar heat into the water tank, warming up the water you are trying to cool.
- HDPE (Plastic): Has a very low conductivity (~0.42 W/mK). A big size plastic cooler acts as a natural insulator. It keeps the water inside the tank colder for longer, even when the unit is sitting in direct sunlight (45°C+), improving the overall Wet Bulb Depression efficiency compared to a metal unit.
Can plastic coolers survive in acidic or chemical-heavy environments?
Absolutely. In industries like Dyeing, Textiles, and Electroplating, acidic fumes cause rapid oxidation (rust) in metal bodies.
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is chemically inert to most acids, alkalis, and solvents. For a chemical factory, a plastic air cooler is the only viable option. While a metal cooler may corrode and leak within 18–24 months in these fumes, a polymer body remains structurally sound for 10+ years, making it the best air cooler for chemical factories.
Why are plastic coolers quieter than metal ones?
Noise pollution is a major concern in commercial spaces.
- The Physics: Metal coolers are "fabricated" (screwed/riveted together). Over time, fan vibrations loosen these joints, causing the metal sheets to rattle and hum.
- The Plastic Advantage: A big size cooler made via Rotomolding is a single, seamless piece of hollow plastic. This structure naturally absorbs and dampens motor vibrations rather than amplifying them. This makes commercial air cooling units made of plastic ideal for noise-sensitive areas like banquet halls, offices, and schools.
Is the "Plastic" used in these coolers eco-friendly?
There is a misconception that metal is always greener.
- The Reality: Metal coolers require annual painting and rust-proofing (chemical waste). Once rusted, the scrap value is low and the material is degraded.
- Recyclability: The "Engineering Plastic" (usually Grade 2 HDPE) used in the biggest coolers is 100% recyclable. At the end of its 15-year life, the body can be shredded and repurposed into pallets or pipes. When you consider the elimination of toxic anti-rust paints and the longevity of the product, a big size plastic cooler often has a lower lifetime environmental footprint.
How does the "Curve" design save electricity?
- The Metal Flaw: Fabricated metal coolers are square boxes with sharp 90° corners. In fluid dynamics, sharp corners create "eddies" (turbulence), which increases drag.
- The Plastic Edge: Molded plastic bodies feature smooth, rounded internal venturis (like a wind tunnel). This reduces internal air resistance. A fan in a plastic air cooler can often throw air 15% further than the same fan in a metal box because it isn't fighting against turbulence. This is the secret to energy efficient large space cooling.
Are plastic coolers safe for the Food & Pharma industries?
- The Risk: Rusted metal surfaces are porous and harbor bacteria/algae roots that are impossible to fully clean.
- The Solution: Rotomolded plastic has a "Class A" smooth finish that is non-porous. It prevents algae roots from penetrating the material. For an industrial air cooler in a food processing plant, this means the unit can be chemically washed down to meet FDA/HACCP hygiene standards - something you cannot do with a rusting metal cabinet.

Maulik Solanki is a seasoned B2B Product Marketing professional specializing in Industrial and Commercial Coolers in the LSV (Large Space Venticooling) segment. With 13+ years of experience, he drives brand building and audience engagement for Symphony’s LSV solutions through integrated offline and online strategies. Backed by an MBA in Marketing and earlier experience as a Regional Marketing Manager in banking, Maulik brings strong skills in sales, advertising, and events. He enjoys exploring new marketing ideas and cooling technologies and writes to help readers understand Symphony’s offerings.

Sourav Biswas is a senior marketing leader heading the LSV (Large Space Venticooling – B2B) marketing function at Symphony Limited. He shapes the brand’s strategic narrative, strengthens market leadership, and ensures excellence across all B2B cooling solutions. With deep expertise in Strategic Marketing, Brand Management, Advertising, and PR, he reviews content with analytical precision and alignment to Symphony’s vision. Passionate about mentoring and tracking B2B trends, Sourav ensures every content piece reflects accuracy, relevance, and strategic depth.






